 |
Medical Basis
Hilotherapy is the product of medical science research, conducted with a focus on the healing processes of injured or traumatised tissue.
Findings on the role of oxygen and nutrient supply
- Surgical interventions or injuries massively disrupt the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the tissue.
- The accelerated metabolic rate causes overheating due to inflammation of the affected tissue, alongside circulatory disturbances.
- Under these circumstances, the need for oxygen surges dramatically.
Consequences
The increased oxygen requirement means that the existing amount of oxygen that actually reaches the affected tissue is insufficient for regeneration.
- This lack of oxygen (ischemia) triggers the death of further cells.
- Results in the release of liquid-binding proteins, which trigger the formation of additional edema.
- Triggers a vicious circle, which leads to damage through hypoxia.
Oxygen Supply and Demand After Trauma
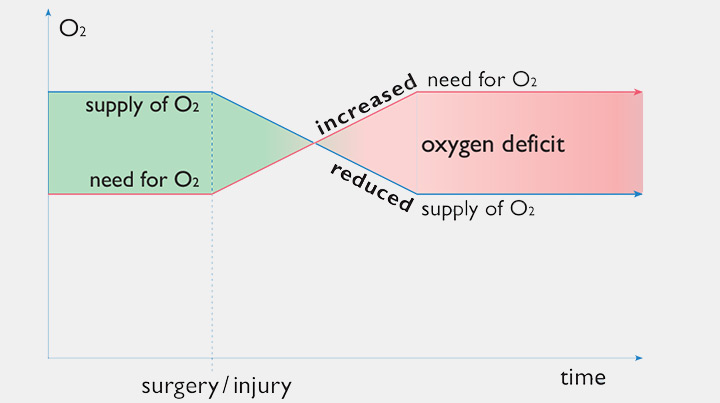
Oxygen deficit: The reduced supply and simultaneous increase in demand results in a deficit, exacerbating tissue damage.
Medical requirement
The oxygen requirement for the damaged tissue has to be reduced.
Therapeutic Response
These findings sparked the development of Hilotherapy. The ideal therapeutic temperature varies depending on indication, so the system can be adjusted to the nearest degree over a spectrum from +10 to +35°C, on the affected portion of the body.
Effect on the oxygen requirement
- Lowering the temperature of the affected tissue by 10°C reduces the metabolism by 50%.
- This also reduces the oxygen requirement.
- The oxygen quantity now suffices for regeneration.
Oxygen Supply and Demand After Trauma and Hilotherapy Application
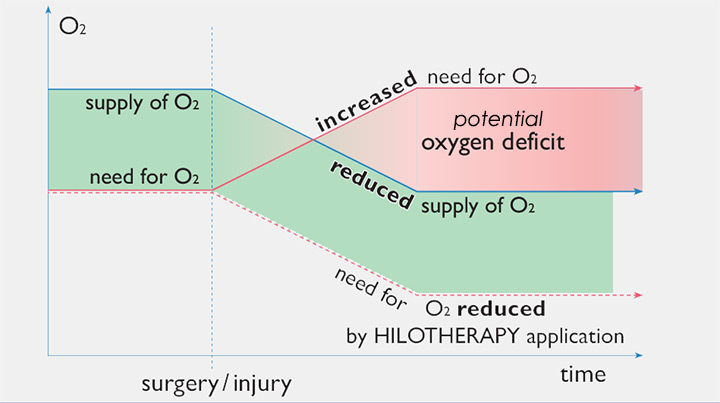
Oxygen adjustment: Hilotherapy reduces the oxygen requirement and paves the way for regeneration.
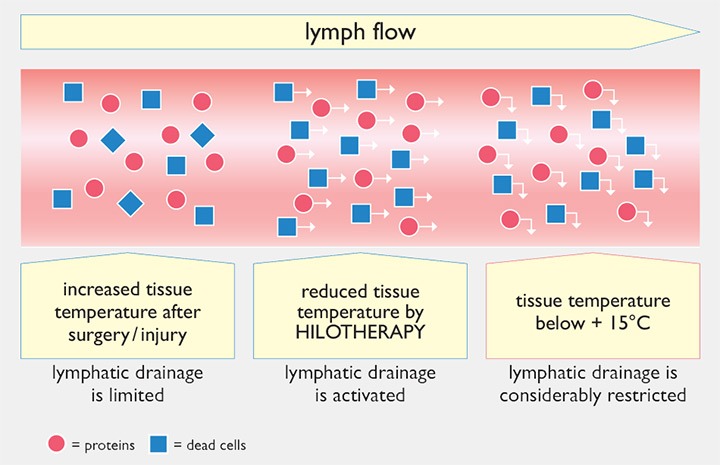
Effect of Hilotherapy on toxin decomposition
- To ensure that damaging materials such as proteins or dead cells are removed via lymph drainage, the tissue temperature must be lowered, accurate to the nearest degree.
- If the tissue temperature drops below +15 °C, the lymph drainage is severely hindered.
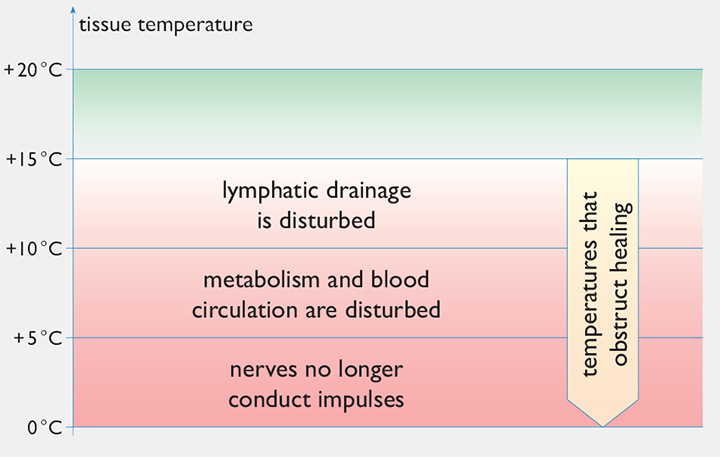
Risks of incorrect tissue temperature
Trauma, either through injury or surgery, causes inflammation. One of the first things that happens is vasodilation, which causes bleeding, bruising and haematoma. There is loss of endothelial integrity, which leads to extravasation of fluids into the extracellular space, causing oedema; and release of inflammatory enzymes, like bradykinin and serotonin, which causes pain.
Cold immediately causes vasoconstriction, which limits the amount of bruising and hopefully bleeding and haematoma. It reduces the amount of extravasation of fluids, and hence reduces oedema. Therefore the cold slows down cellular metabolism as well as cellular enzyme activity and so reduces pain.
The vasoconstrictive effect of cold reaches a maximum at about 15ºC, below 15ºC there is aparadox vasodilation, which is largely explained by paralysis of the endothelial-smooth muscles and a possible nerve conduction block of the nerve fibres that cause vasoconstriction.
Hilotherapy is therefore a much more effective therapy than ice, gel packs and ice packs... because with ice and a temperature that is below 15ºC the positive effects of cold are negated.
|